IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
Source:- Google.com.pk
ITKiDuniyaa Define Fdisk?
For computer file systems, fdisk (for "fixed disk") is a command-line utility that provides disk partitioning functions. In versions of the Windows NT operating system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems.
Implementations
DOS and Windows
IBM introduced fdisk, Fixed Disk Setup Program version 1.00, with the March 1983 release of the IBM PC/XT, the first PC to store data on a hard disk, and the IBM Personal Computer DOS version 2.0. Version 1 could be used to create one FAT12 DOS partition, delete it, change the active partition or display partition data. fdisk writes the master boot record, which supported up to four partitions. The other three were intended for other operating systems such as CP/M-86 and Xenix, which were expected to have their own partitioning utilities as fdisk did not support them.
In August 1984, PC DOS 3.0 added FAT16 partitions to support larger hard disks more efficiently.
In April 1987, PC DOS/fdisk 3.30 added support for extended partitions, which could hold up to 23 "logical drives" or volumes.
Support for FAT16B was added with Compaq MS-DOS 3.31, and later became available with MS-DOS/PC DOS 4.0.
Most DOS fdisk programs, including the fdisk program that came with the original Windows 95, are only capable of creating FAT partitions of types FAT12, FAT16 and FAT16B.
A derivative of the MS-DOS fdisk was provided with Windows 95, Windows 98, and later Windows Me. Only those fdisk versions shipping with Windows 95B or later are able to manipulate FAT32 partitions. Windows 2000 and later do not use fdisk, they have the Logical Disk Manager feature, as well as DiskPart.
Unlike the fdisk programs for other operating systems, the fdisk programs for DOS and Windows 9x/Me not only alter data in the partition table, but will also overwrite many sectors of data in the partition itself.[citation needed] (However, to create an extended partition any partition editor must put extended boot records before each logical drive on the disk.) Users must be sure the correct disk/partition has been chosen before using a DOS/Windows fdisk for partitioning. The fdisk /mbr switch is undocumented but well known for repairing the master boot record.
FreeDOS
The implementation of fdisk in FreeDOS has many advanced features and is free software.
Unix-like systems
Linux needs at least one partition, namely for its root file system. It can use swap files and/or swap partitions. Almost all Linux installations have a second partition dedicated as swap space.
Other Intel based Unix-like systems typically use a more elaborate arrangement. BSD-derived systems use a disklabel as their primary method of identifying distinct sections of the disk, usually termed slices. These slices may or may not correspond to partitions enumerated in the master boot record. A typical arrangement is for the entire Unix system to have a single partition allocated to it which is then subdivided into distinct slices for each filesystem and the swap area. Other partitions outside this dedicated one may be legitimately referenced in a disklabel - this is particularly true in dual boot scenarios, where it is desired that the Unix system be able to access partitions used by other operating systems residing on the same machine.
This approach is not mandatory since the MBR and bootlabel are two distinct records - it is technically possible (but not recommended) for the disklabel to describe a filesystem on an area of the disk that the MBR regards as unused. Regardless of the correlation between the two records, the 'entire disk' slice of the disklabel usually corresponds to the entire physical disk and not solely to the dedicated partition. In order to eliminate any possibility of confusion caused by these two (possibly contradictory) records, the sysadmin of these systems may elect to eliminate the master boot record from the disk. However, a disk laid out this way is unusable by any other operating systems.
The situation with System V-derived systems is similar to that with the BSDs, although the terminology usually used differs slightly. In this instance a single partition is subdivided using the divvy command, and such areas are often simply referred to as divisions.
On older Intel compatible hardware, the BIOS that boots the system can often only access the first 1024 cylinders of the disk. For this reason a separate filesystem, often of only a few megabytes, is often created at the start of the disk to store the kernel image and a few auxiliary files needed at boot time, ensuring that they are readable by the BIOS. Once the kernel is loaded and has taken over responsibility for disk activity, the filesystem is typically mounted on /boot or /stand. There may also be reasons of security, ease of administration and backup, or testing, to use more than the minimum number of partitions.
OS/2
OS/2 shipped with two partition table managers up until version 4.0. These were the text mode fdisk and the GUI-based fdiskpm. The two have identical functionality, and can manipulate both FAT partitions and the more advanced HPFS partitions.
OS/2 versions 4.5 and higher (including eComStation) can use the JFS filesystem as well as FAT and HPFS, and replace fdisk with the Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
ITKiDuniyaa Explains Fdisk In Simple Words
FDISK is a utility, included in all versions of MS-DOS and Windows, for formatting (preparing) a hard disk drive to hold data and to logically partition the disk, specifying and naming major portions of it for different uses. FDISK is used to prepare and partition a brand new hard drive, and typically most personal computers today arrive with the drive already partitioned and loaded with the operating system and perhaps other software. A typical personal computer today arrives with a single partition that is addressed by the operating system as the logical C drive. (Some PCs also have one or two diskette drives addressed as the A and B drives. PCs with CD-ROMs also usually address the CD-ROM as the D drive. But a hard disk drive can be divided into and addressed as several "logical" drives, or partitions.)
In addition to setting up a new hard disk drive, FDISK is used for repartitioning the hard drive when you want to change something. For example, a computer can be set up as a dual boot system, with one operating system (for example, Windows 2000) in one partition and another operating system (for example, Linux) in another partition. Disk partitioning is also commonly used on LAN servers, where different sets of users share different files and applications. The maximum partition size in the first version of DOS to use FDISK was 16 megabytes. Recent Windows systems support hard drives up to 2 terabytes (2,000 gigabytes) in size!
If you need to repartition your current hard drive, be sure to back up all data because it will be lost when you use FDISK. Be careful to follow the documented Microsoft and manufacturer directions.
The age of your computer and the operating system you use determines how difficult the hard drive installation will be. The Basic Input Output System (BIOS) in computers manufactured before 1994 does not support drives larger than 512 MB, which causes FDISK to display larger hard drives as only 512 MB in size. It is necessary to use disk management software that helps an older BIOS version to recognize a hard drive larger than 512 MB. Disk management software is usually included with your new hard drive or free upon request from the hard drive manufacturer. You can also purchase a BIOS upgrade such as an EPROM chip, flash memory BIOS software, a controller card, or a card with a BIOS chip on it depending on the manufacturer's recommendation. Depending on your operating system, you may have to create multiple partitions in order to use your hard drive's full capacity:
DOS version 6.22 and later supports drives greater than 8.4 GB. Versions earlier than 6.22 do not.
Windows 95A does support drives larger than 8.4 GB, but you have to partition the drive into at least four partitions depending on the hard drive's size because of FAT 16 file system's limitations used by Windows 95A. Windows 95B supports FAT 32, which allows one large partition on new hard drives and supports hard drives up to 2,000 GB in size.
The first and later editions of Windows 98 support FAT 32 and hard drives up to 2,000 GB.
Windows NT version 5.0 and later also supports large hard drives.
FDISK has its limitations. You can't move applications from one partition to another without uninstalling and reinstalling the software. FDISK erases all data on your hard drive. And you can't delete or create new partitions without going through the entire FDISK and formatting process again. However, special partitioning software such as PartitionMagic can be used instead of FDISK. Partitioning software allows you to create, delete, and resize partitions without losing your data. You can move applications from one partition to another without uninstalling and reinstalling the application. You can hide partitions to protect data from other users. You can also use partitioning software as a boot manager. A boot manager allows you to install and use more than one operating system easily. Partition software also eliminates the need for a BIOS upgrade in older computers.
ITKiDuniyaa Explains Fdisk In Short Words
A DOS and Windows utility that prepares a hard disk for formatting by creating one primary partition on the disk.
ITKiDuniyaa Define Formatting?
To format an unformatted floppy fresh from the box, put it into drive A or B and type:
format a: or format b:
and answer the prompts.
FLOPPY DISK SIZES
There are four floppy disk capacities:
Diameter Capacity Name
5.25" 1.2MB High density
5.25" 360KB Low density (Double Density)
3.5" 1.44MB High density
3.5" 720KB Low density (Double Density)
Higher-density drives can read and write low-density disks. But to format a low-density disk in a high-density drive, you must modify the command as follows.
FORMATTING 5.25" DISKS
To format a 360K disk in a 1.2M drive, type:
format a: /4 All versions
format a: /f:360 DOS 4.01 and up
Caution!
360K disks formatted on very early 1.2MB drives may cause reading problems.
FORMATTING 3.5" DISKS
To format a 720KB disk in a 1.44MB drive, type:
format a: /n:9 /t:80 All versions
format a: /f:720 DOS 4.01 and up
To format a 1.44M disk in a 2.88M drive, type:
format a: /f:1.44
REFORMATTING A FLOPPY (As of DOS 5)
The /q switch causes Format to bypass checking for bad sectors. To quickly reformat a formatted disk that you know is OK, type:
format a: /q
Previous to DOS 5, the format program completely formatted a floppy losing all data if previously formatted. As of DOS 5, Format creates a "safe format" by saving additional data on the disk. This takes a bit longer but allows the disk to be unformatted. Since you will not have to unformat blank disks, you can format "unconditional" and speed up the format process with the /u switch:
format a: /u
Also previous to DOS 5, any bad sector on a diskette eliminated the entire track. As of 5, only that sector is marked as bad.
CREATING A BOOTABLE FLOPPY
To format a floppy and make it "bootable" by copying DOS from the hard disk onto it, type:
format a: /s
The DOS COMMAND.COM file is also necessary on the bootable floppy. Starting with DOS 5, the Format command copies COMMAND.COM to the floppy automatically. In DOS 4.01 and earlier, you have to copy COMMAND.COM manually.
Formatting a Hard Disk Is Three Steps
WHAT YOU DO WHAT YOU USE
1. Low-level format Low-level format program
2. Create partitions FDISK.EXE program
3. High-level format FORMAT.COM program
LOW-LEVEL FORMAT
All IDE hard disks and most SCSI disks are already low-level formatted at the factory. Sometimes the SCSI host adapter (controller card) requires that a low-level format be performed on each new SCSI drive that is added to the system. Read the instructions that come with your host adapter to be sure. The low-level SCSI format utility is typically built into the host adapter and is launched by pressing a certain key immediately after the computer is turned on.
CREATE PARTITIONS WITH FDISK
Every hard disk must be partitioned after it is low-level formatted. Even if one drive letter serves the entire disk, you must use the Fdisk utility to create a primary partition for that disk. If your DOS version cannot support the full size of the disk, or if you want to divide up your disk for your own storage reasons, you first make a primary partition and then an extended partition for the logical drives to reside in.
DOS Disk size
Version Supported
3.3 32MB
4.0 512MB
5.0 2GB
6.0 2GB
To Fdisk your C: drive, boot the computer with a bootable floppy in drive A:, which also contains the FDISK.EXE program. At the A: prompt, type:
A:\>fdisk
Select from the options. In Fdisk, drives are not letters, they are numbered (1, 2, etc.). In Fdisk, the active partition is the one you boot from and is assumed to be the C: drive. If it is not, you can change that in Fdisk.
If you want to Fdisk a second or subsequent hard disk, load Fdisk from the C: drive:
C:\>fdisk
HIGH-LEVEL FORMAT
The final step is to run the Format command for each logical drive (C:, D:, etc.). This step creates the directory structure and FAT tables and places startup data in the boot sector.
To format your C: drive, boot the computer with a bootable floppy in drive A:, which also contains the FORMAT.COM program. Use the /s switch to transfer DOS to the hard disk as soon as the formatting is completed. To format drive C, type:
A:\>format c: /s
To format a second or subsequent hard drive, load Format from your C: drive. For example, to format drive D:, type:
C:\>format d:
How to Use The Fdisk Tool To Partitions Or Repartitions A Hard Disk [Tutorial Provided By ITKiDuniyaa]
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 1
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 2
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
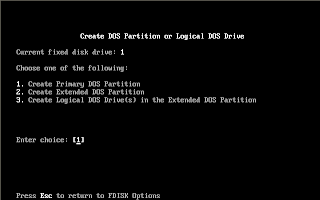
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 3
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 4
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 5
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 6
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 7
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 8
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Partition Making With Fdisk Step 9
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
How To Use The Format Tool To Formatting Drives [Tutorial Provided By ITKiDuniyaa]
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Drives Formatting With Format Command Step 1
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Drives Formatting With Format Command Step 2
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners
ITKiDuniyaa Drives Formatting With Format Command Step 3
For More Latest Tech Updates, Stay With Us On itkiduniyaa.blogspot.com
IT KI DUNIYAA | Reading for information | Needs of All Students And learners